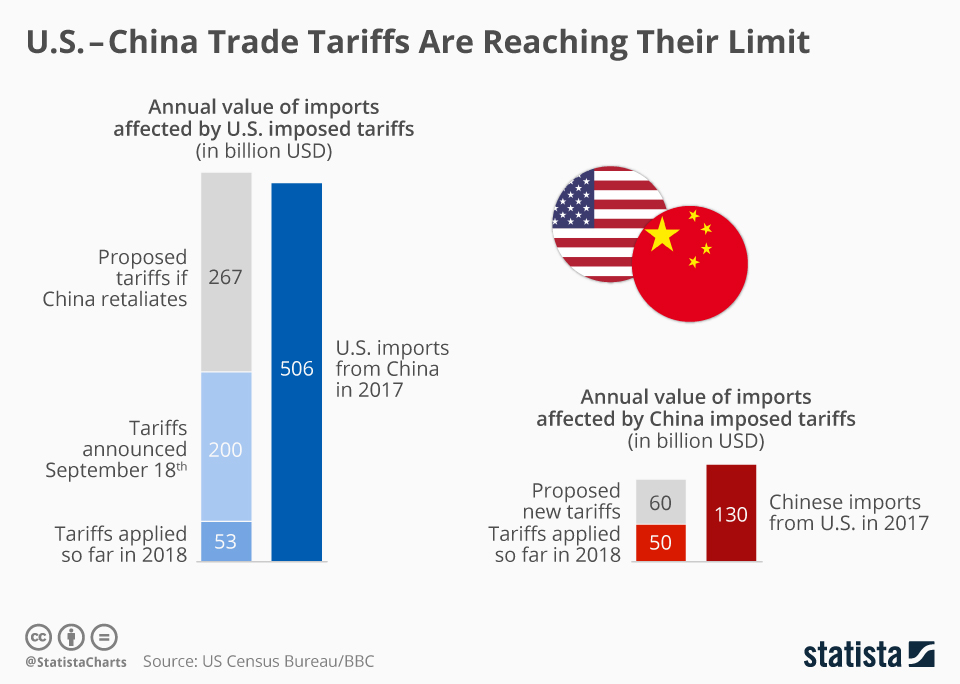
China tariffs have become a focal point in the ongoing discourse surrounding the US-China trade war, raising concerns over the impact of tariffs not only on the Chinese economy but also on global trade relations. As tensions escalate, experts warn that imposing heavy tariffs could lead to significant supply chain disruptions, ultimately resulting in higher prices for American consumers. In this delicate balancing act, the potential fallout extends beyond economic consequences, potentially altering the dynamics of trade alliances and relations with U.S. allies. While the intention behind such tariffs might appear to protect domestic interests, the ripple effects could inadvertently bolster China’s position on the world stage. This complex interplay highlights the stakes involved in tariff policies and their far-reaching implications for both nations and the global economy as a whole.
In recent discussions on trade dynamics, the issue of levies imposed on Chinese imports has emerged as a pivotal topic amid the broader US-China economic tensions. These financial barriers could shift the landscape of international commerce, as many analysts fear that they might inflate consumer costs and complicate existing supply chains. Concurrently, reallocating trade partnerships could weaken traditional alliances, allowing nations to reassess their collaborations. The multifaceted consequences of these import taxes are not limited to mere economic statistics but extend to political ramifications, as nations navigate this uncertain terrain. Understanding the full scope of these tariffs is crucial for grasping the underlying currents of global trade relations.
Understanding the Consequences of China Tariffs
The prospect of implementing new tariffs on Chinese goods raises considerable concerns beyond just the immediate economic impact. Economists predict that China tariffs designed to protect American jobs could inadvertently lift prices for consumers domestically. As companies begin to face higher costs due to tariffs, they often pass these expenses onto consumers in the form of increased prices. This phenomenon could create inflationary pressure in the U.S. economy, leading to diminished purchasing power for American households.
Furthermore, tariffs could ignite a wider trade conflict known as the US-China trade war, disrupting existing supply chains. American companies heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing may experience interruptions in the production of goods, leading to delays and shortages. These supply chain disruptions not only hinder American businesses but also lead to an increased risk of job losses, undermining the intended protective advantage of tariffs.
The Impact on Global Trade Relations
China’s reaction to U.S. tariffs could reshape global trade relations significantly. As noted by experts, retaliatory measures may not be limited to economic responses but could extend to political alliances. For instance, if U.S. tariffs lead to a decline in trade between the U.S. and China, Beijing might seek stronger ties with European or Southeast Asian nations, forming new strategic partnerships that could isolate the United States in global economic discussions. This shift could ultimately harm U.S. global influence and diplomatic leverage.
Moreover, as China’s economy looks to adapt to the potential fallout from tariffs, it could intensify efforts to diversify its trade partners. This shift may result in a fragmented global market, where countries are compelled to choose sides in the U.S.-China conflict. Such realignments in global trade relations could have long-lasting effects on international diplomacy and economic cooperation.
China’s Economic Resilience Amid Tariffs
Despite the looming threat of heightened tariffs, there are signs of resilience in the Chinese economy, which has demonstrated adaptability in the face of external pressures. China has strategically engaged in initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) to bolster its economic ties with developing countries, presenting opportunities for growth even if trade with the U.S. falters. This systematic approach to expanding its global footprint indicates China’s willingness to invest in emerging markets as a means of offsetting U.S. tariff impacts.
Moreover, China’s focus on technological advancements and the promotion of new sectors, such as electric vehicles, may position it to thrive even amid stringent tariffs. As the nation pioneers innovations in high-tech industries, it can potentially reduce its dependence on exports to the U.S. and tap into alternative markets, illustrating the complexity of the economic landscape where traditional power dynamics are continually shifting.
Supply Chain Disruptions: A Looming Reality
The potential for supply chain disruptions looms large as new tariffs threaten established shipping routes and production schedules. Many industries, including technology and automotive, rely on intricate networks that span across countries. If tariffs impede this flow, businesses could face significant operational challenges, leading to production delays and increased costs that trickle down to consumers. Companies may need to re-evaluate their supply chains and seek out alternative sources, which could be a complex and costly endeavor.
In this evolving scenario, businesses may also be confronted with difficult decisions regarding employment and investment. Supply chain disruptions could stem not only from immediate tariff impacts but also from long-term shifts in manufacturing trends. Therefore, companies that react proactively by diversifying their supply bases may better mitigate risks associated with tariffs, ultimately shaping the future landscape of global commerce.
Negotiations and the Future of U.S.-China Trade
Amid the backdrop of escalating tariffs, the potential for renewed negotiations between the U.S. and China remains a crucial element to consider. The idea is that tariffs might not only serve as punitive measures but could also be leveraged as negotiating tools to arrive at more constructive trade agreements. Economists emphasize that a clear and mutually beneficial agreement could stabilize relations and foster a conducive environment for trade between the two economic powerhouses.
However, the path to negotiation is fraught with complexities. For effective dialogue to occur, both sides must be willing to make concessions and engage in good faith discussions. If tariffs are perceived merely as a means to exert pressure, it may lead to further entrenchment of adversarial positions, prolonging the trade conflict. Therefore, it’s vital for stakeholders on both sides to prioritize diplomacy to prevent economic fallout from escalating further.
Increase in U.S. Consumer Prices Due to Tariffs
One of the most immediate and tangible effects of the China tariffs is the likelihood of increased prices for consumers across the United States. When American producers face higher import costs due to tariffs, these expenses are typically passed down to consumers in the form of higher prices for goods. Everyday items—from electronics and appliances to clothing—could become significantly more expensive, effectively diminishing the purchasing power of U.S. households.
The impact on consumer prices raises important questions about the long-term viability of protectionist trade measures. If tariffs lead to widespread price increases, consumer sentiment may shift against these policies, prompting potential backlash against governmental decisions. Such sentiment could have ramifications for voting behavior and overall economic stability, underscoring the need for careful consideration of tariff implementation.
Alternatives to Chinese Manufacturing
As U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods tighten, there is a growing urgency for American companies to explore alternatives to Chinese manufacturing. Countries like India and Vietnam are emerging as viable options for relocating supply chains; however, the transition is not without complications. For instance, while India has a burgeoning market with potential labor advantages, it might take years to scale its manufacturing capacity to meet global demand effectively.
Meanwhile, Vietnam presents an attractive alternative due to its proximity to China and existing manufacturing ecosystems. Still, this close geographical tie may introduce risk factors involving supply chain reliability. The exploration of new manufacturing locales emphasizes the interconnected nature of global trade and the challenges of swiftly pivoting operations to minimize disruptions caused by tariffs.
China’s Strategy for Domestic Economic Growth
In light of impending tariff strategies, China is focusing on stimulating domestic economic growth to reduce reliance on exports. Increasing consumption has long been a target for the Chinese government, which is now seeking sustainable pathways to foster an internal market that can thrive independent of international trade pressures. This pivot towards bolstering domestic consumption could help offset the negative impacts of tariffs on its global trade activities.
Yet, moving from an export-driven economy to one centered on domestic consumption presents unique challenges. Policymakers face the task of encouraging urbanization and consumer spending while simultaneously managing the risks associated with a trade surplus that has historically defined China’s economic model. The success of this strategy hinges on effective policymaking and the willingness of the populace to engage in increased consumption.
The Potential for Economic Isolation
Should the U.S. maintain or escalate tariffs on China, the long-term consequences could lead to economic isolation for the United States in global markets. If China and its trade partners respond by forming closer cooperative ties, especially amidst increased tariffs from the U.S., this could disrupt established trading patterns and erode America’s position as a dominant player in global economics. The result may be a fragmented global economy where nations pursue self-sufficiency or realign with alternative trading partners.
Such isolationist tendencies could have far-reaching implications for American businesses that rely on international markets for growth and expansion. As consumers in the U.S. potentially face higher prices and reduced choices due to tariffs, the risk of economic backlash becomes a notable concern. Thus, fostering collaborative trade relationships, as opposed to extensive tariffs, could prove more beneficial for maintaining robust economic ties.
Frequently Asked Questions
What impact do China tariffs have on the US-China trade war?
China tariffs significantly influence the US-China trade war by intensifying economic tensions between the two nations. The imposition of tariffs often leads to retaliatory measures, which can further escalate trade conflicts and disrupt global trade relations.
How do China tariffs affect the China economy?
China tariffs can negatively impact the China economy by increasing the cost of exports, thereby reducing competitiveness in the U.S. market. This can lead to decreased sales and potential job losses in export-driven industries that rely heavily on American consumers.
What are the potential supply chain disruptions caused by China tariffs?
The imposition of China tariffs can cause significant supply chain disruptions, as companies face higher costs for raw materials and components sourced from China. These disruptions can lead to delays in production and increased prices for consumers, affecting the overall efficiency of global supply chains.
How might China tariffs influence global trade relations?
China tariffs could reshape global trade relations by encouraging countries to seek new trading partners to avoid higher costs associated with U.S. tariffs. This shift may foster alliances among nations affected by similar tariff policies, ultimately altering the dynamics of international trade.
What is the relationship between China tariffs and US consumer prices?
China tariffs are likely to lead to higher consumer prices in the U.S. as businesses pass on the increased costs of imported goods to consumers. This can reduce disposable income and impact overall consumer spending, leading to broader economic implications.
How do China tariffs pose a risk of labor shortages in the U.S.?
The enforcement of China tariffs may contribute to labor shortages in the U.S. as companies face increased costs and may opt to reduce hiring or layoffs. This scenario can create gaps in the labor market, particularly in sectors dependent on imports from China.
What strategies is China employing in response to U.S. tariffs?
In response to U.S. tariffs, China is strategizing to diversify its export markets and enhance its domestic economy by boosting consumer spending. Initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative aim to strengthen economic ties with other countries while mitigating the impact of U.S. tariff policies.
What are the long-term effects of China tariffs on international relations?
The long-term effects of China tariffs on international relations may include a reconfiguration of alliances, as countries affected by tariffs might collaborate to present a united front against U.S. trade policies. This shift could result in new global economic alliances that challenge U.S. dominance.
Could China’s economy rebound despite high tariffs?
Despite high tariffs, China’s economy could rebound by focusing on emerging markets through initiatives like the Global Development Initiative. By enhancing trade with countries in Southeast Asia and Africa, China may partially offset losses incurred from U.S. tariffs.
How are China tariffs impacting U.S. businesses and consumers?
China tariffs are impacting U.S. businesses by raising import costs, which can lead to increased prices for consumers. Businesses may also face challenges in maintaining supply chains that depend on Chinese goods, affecting their overall competitiveness.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of Tariffs on China | Tariffs could severely hinder China’s global export ambitions, particularly to the U.S., which is crucial to their economy. |
| Impact on U.S. Economy | Higher tariffs could raise prices for American consumers and disrupt supply chains, leading to a potential economic slow down. |
| China’s Response | China may see these tariffs as a negotiation tactic from the U.S. and could respond with their own strategies to safeguard their economy. |
| Alternative Markets for China | China is focusing on markets in Europe and developing economies to mitigate reliance on U.S. imports. |
| Potential Allies for China | New tariffs could push China closer to traditional U.S. allies, fostering collaborations against U.S. trade policies. |
Summary
China tariffs could potentially reshape not only trade relationships but also foreign alliances. The imposition of these tariffs is seen as a threat to China’s economy, possibly leading to higher costs for American consumers and supply chain disruptions. While this policy aims to hurt Beijing’s economic structure, it may also trigger unintended consequences, like strengthening China’s ties with traditional U.S. allies and creating economic woes for the U.S. Ultimately, navigating this complex global trade environment requires careful consideration of these potential outcomes.